Oral cancer or mouth cancer represents a variety of cancers that can manifest anywhere in the mouth, encompassing areas like the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and pharynx (throat). The severity of oral cancer underlines the importance of early detection and prompt treatment. Learn more about oral cancer from the American Cancer Society.
The Role of Tobacco and Alcohol
Tobacco, in all its forms, significantly increases the risk of oral cancer. Concurrently, alcohol, especially when consumed excessively, has been linked to a heightened oral cancer risk. These two factors combined can have a compounding effect on oral cancer development. Find more details about these risk factors on the American Cancer Society’s page.
The Impact of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Specific variants of HPV, a sexually transmitted infection, have been associated with a higher incidence of oral cancers, predominantly oropharyngeal cancers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides more information about this connection.
Oral Sores and Lumps
Persistent Oral Discomfort or Pain
Another telltale symptom of oral cancer is enduring oral discomfort or pain. This discomfort may manifest as a lingering sore throat, a sensation of something caught in the throat, or difficulty swallowing or chewing. There might also be a shift in the way your teeth or dentures fit together – a change that is inexplicable by dental health variations. The Mayo Clinic provides a more comprehensive list of oral cancer symptoms, emphasizing the importance of early detection.
Quitting Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups
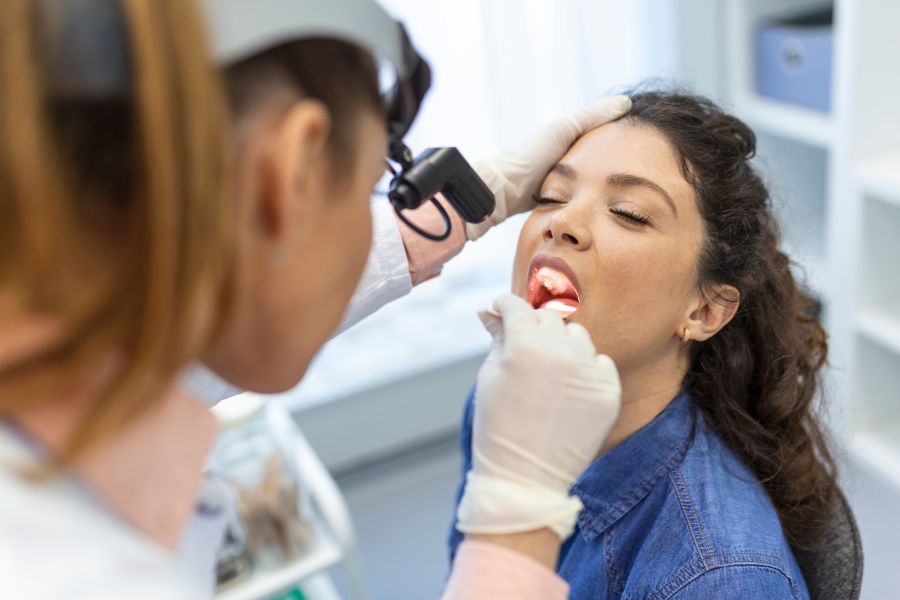
Regular dental check-ups form the cornerstone of early detection and prevention of oral cancer. These check-ups usually include a comprehensive oral cancer screening, which involves a thorough examination of your oral cavity and connected tissues. Dentists are often the first healthcare professionals to spot early signs of oral cancer, underscoring the importance of routine dental visits. Further information on the role of dental check-ups in oral cancer prevention can be found at the American Dental Association.
HPV Vaccination
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection, with certain strains significantly associated with the development of oral cancer. Particularly, HPV type 16 has been linked to oropharyngeal cancer, a type of head and neck cancer. The HPV vaccine, which protects against the high-risk HPV types, has shown to be effective in preventing the infections that may lead to oral cancers. It is typically recommended for preteens, but can also be given at other ages based on a healthcare provider’s advice. This underlines the role of HPV vaccination as a preventive strategy against oral cancer.
Oral cancer, like many types of cancer, can be life-altering. However, the power of prevention and early detection can’t be overstated. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including quitting tobacco, limiting alcohol, and prioritizing oral hygiene, plays a significant role in lowering your risk of oral cancer. Additionally, regular dental check-ups are critical for early detection and successful treatment outcomes.
The HPV vaccine is an important preventive measure against certain types of oral cancer. Moreover, an understanding of the symptoms, such as persistent oral discomfort, sores, or lumps in the mouth, can aid in early detection.
Keep in mind that while these symptoms may not definitively point to oral cancer, they necessitate prompt medical attention. As the saying goes, “Prevention is better than cure.” Be proactive about your oral health – it could save your life.